CCAT Grade 6 Level 12
Enrollment in a gifted and talented program, students must sit for the Canadian Cognitive Abilities Test (CCAT Level 12) This test is designed to determine how well a 12-year-old can reason and solve unfamiliar situations. The beauty of the test is that it does not test how well a child memorizes information or how well they are doing in school. The CCAT Level 12 is built to assess your child’s ability to see patterns and relationships between shapes, as well as other cognitive exercises.
What’s on the Test
Grade 6 CCAT has 176 questions, covering three sections, or batteries, covering nonverbal, verbal, and quantitative abilities. Every battery is further subdivided into three subsections, for a total of nine subsections. Your child’s school will determine whether the candidates sit for the three batteries in once session, or separately.
Verbal Battery
The Verbal Battery of the CCAT (Canadian Cognitive Abilities Test) measures a student’s ability to understand and reason with concepts framed in words. This includes skills like verbal reasoning, vocabulary, analogies, and sentence completion. These questions test relationships between words, identifying patterns, and applying logic.
Verbal Analogies
1. Nest : Bird Cave :: _____
a. bear
b. petal
c. house
d. dog
Answer: A
A Bird lives in a nest, the way way a bear lives in a cave.
2. Teacher : School :: _____ : _____
a. Businessman : Money
b. Waitress : Coffee Shop
c. Dentist : Tooth
d. Fish : Water
Answer: B
A teacher works in a school in the same way a Waitress works in a coffee shop.
3. Pebble : Boulder :: Pond : _____
a. Ocean
b. River
c. Drop
d. Rapids
Answer: A
A boulder is a very large pebble – both are rocks, in the same way an ocean is a very large pond – both are very bodies of water.
Sentence Completion
1. The meeting was __________ because it determined the company’s future.
A) sparse
B) peculiar
C) crucial
Answer: C) crucial
The word “crucial” means extremely important or decisive. Since the meeting determined the company’s future, it was important or “crucial” to its success.
2. In the desert, vegetation is often __________ due to the lack of water.
A) crucial
B) peculiar
C) sparse
Answer: C) sparse
The word “sparse” means thinly scattered or in small amounts. Vegetation in the desert is typically limited because of the arid environment, making “sparse” the correct choice.
3. Her behavior was __________ at the party, and many people found it hard to understand.
A) crucial
B) sparse
C) peculiar
Answer: C) peculiar
“Peculiar” refers to something that is strange or unusual. Since her behavior was difficult for others to comprehend, it can be described as “peculiar.”
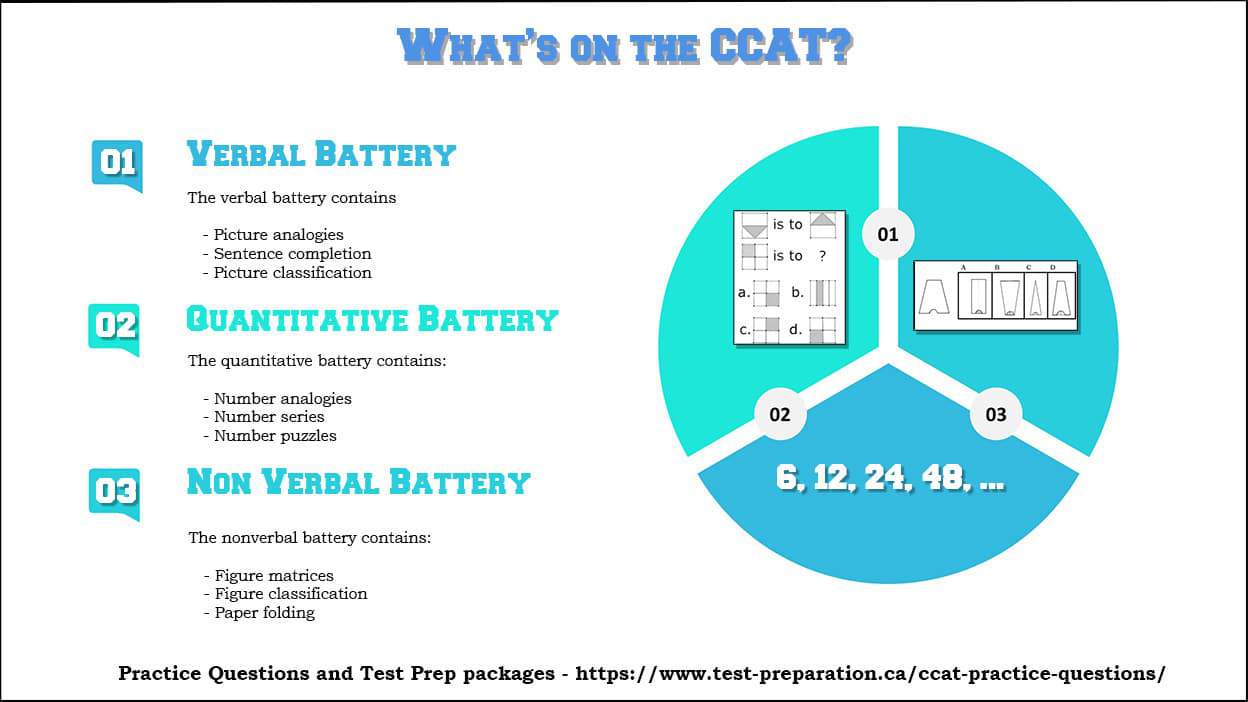
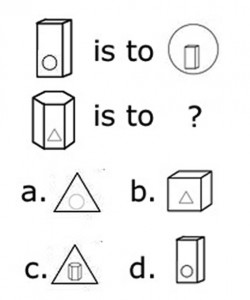
Nonverbal Battery
The Nonverbal Battery presents the test taker with geometric shapes and figures, and asks them to identify relationships between pictures in a matrix, determine how a shape will look when folded or unfolded, and recognizing patterns in a set of shapes and choosing the next figure in the sequence.
Figure Classification
Test-takers are presented with three shapes lined up together. To answer, test-takers must select a fourth shape that matches the category of the three shapes.
Directions: In each of the following questions, select the choice that does not belong with the other three.
1.
2.
3.
1. When the two longest sides touch what will the shape be?
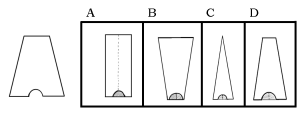
Answer: D
2. When folded into a loop, what will the strip of paper look like?
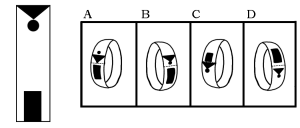
Answer: A
Folding Practice – Visual Acuity
Number Series
Test-takers are given a series of numbers that follow a predetermined rule. They must choose a final number from the choices to complete the series.
1. Consider the following series: 6, 12, 24, 48. What number should come next?
a. 48
b. 64
c. 60
d. 96
Answer: D
The numbers double each time.
2. Consider the following series: 5, 6, 11, 17. What number should come next?
a. 28
b. 34
c. 36
d. 27
Answer: A
Each number is the sum of the previous two numbers.
3. Consider the following series: 26, 21, …, 11, 6. What is the missing number?
a. 27
b. 23
c. 16
d. 29
Answer: C
The numbers decrease by 5 each time.
Quantitative Battery
Number Puzzles
Test-takers are presented with a mathematical equation with a missing number. The equation will be solved by selecting a number that fits the gap and completes the equation.
Example Questions
1. 2 + ___ = 9
a. 7
b. 3
c. 6
d. 8
Answer: A
1. 2 + 7 = 9
2. (3 X 4) – 5 = ___
a. 17
b. 7
c. 12
d. 15
Answer: B
(3 X 4) – 5 = 7
3. (8 X 2) X (2 X 3) ___
a. 60
b. 72
c. 96
d. 92
Answer: B
(8 X 2) X (2 X 3) = 72
Number Analogies
Test-takers are given a pair of numbers and must decide the relationship between the numbers. They are then presented with another number missing its pair. Test takers must apply the relationship from the first pair to complete the second pair.
Example Questions
1. 1 is to 2 as 3 is to:
a) 4
b) 5
c) 6
d) 7
Answer: a)
Just as 1 increases by 1 to become 2, 3 increases by 1 to become 4.
2. 2 is to 4 as 3 is to:
a) 5
b) 6
c) 7
d) 8
Answer: b)
Just as 2 is doubled to become 4, 3 doubled is 6.
3. 5 is to 10 as 6 is to:
a) 11
b) 12
c) 13
d) 14
Answer: b)
Just as 5 is doubled to become 10, 6 doubled is 12.
Click here for CCAT Grade 6 practice questions
CCAT Grade 6 Score Report
The CCAT level 12 Score Report has three scores detailing results of the test and the general cognitive ability of each student. Each score is the sum of the results from the quantitative, nonverbal, and verbal sections. Each report will have an Age Percentile Rank (APR) score that ranks all candidates in a specific age group, a Grade Percentile Rank (GPR) that compares students according to other candidates on their grades, and a Stanine (S) score. A stanine score shows every student’s learning aptitude and is set between 1 and 9 with 9 being the highest possible score, 5 being average, and 1 being the lowest. APR ranks 12-year-old candidates within their age group.
Test Tips
- Use the scratch paper provided effectively. A scratch paper is an important tool for students who prefer thinking out loud. Although students are not allowed to talk during the exam, they have permission to write down their thought processes. Ensure that you familiarize your child with scratch papers as they practice by letting them note down their thinking.
- Do not spend a lot of time on a single question. Students need to answer all the questions in a reasonable amount of time as the exams are timed. Encourage your child to spread their time on all questions evenly. When handling difficult questions, advise them to give the first answer they think of and come back to the question later if time allows it.
Date Published: Wednesday, April 27th, 2022
Date Modified: Tuesday, March 4th, 2025