Purpose of Mechanical Comprehension Tests
Mechanical comprehension tests serve the purpose of assessing your knowledge of mechanical and technical concepts, as well as their spatial relations and logical thinking skills. These tests are commonly used in the recruitment process for both engineering and non-engineering roles.
By evaluating one’s understanding of mechanical principles and basic physical concepts, these tests provide employers with valuable insights into an individual’s ability to comprehend and apply mechanical reasoning skills. They measure an individual’s aptitude in understanding simple machines, mechanical processes, and the physical forces that govern them. crucial in technical roles where the understanding of three-dimensional diagrams and blueprints is essential.
Jobs that use Mechanical Aptitude Entrance Tests
Mechanics
Most types of mechanics need a solid understanding of mechanical systems and concepts to install, maintain, and repair these systems as well as diagnose and fix problems.. Types of mechanics include, automotive, aircraft mechanics, industrial machinery mechanics, and diesel mechanics.
Technicians
Technicians, such as HVAC technicians, Marine technicians, Elevator technicians, and robotic technicians require extensive knowledge of mechanical concepts
Other Professions
Heavy Equipment Operator. Heavy equipment operators operate and maintain large machinery used in construction, mining, and other industries. They must have a good understanding of mechanical systems and be able to troubleshoot and perform basic maintenance tasks.
Power Plant Operator. Power plant operators oversee the operation and maintenance of power generation equipment, such as turbines and generators. They need to understand the mechanical components of these systems and be able to identify and resolve issues.
Start Practicing
Mechanical Aptitude Online Course — Mechanical Aptitude Paperback (Amazon) — Mechanical Aptitude PDF Download
Types of Questions on Mechanical Comprehension Tests
Levers
A lever is a rigid bar or beam that rotates around a fixed point, the fulcrum. There are three types of levers based on the position of the effort (input force) and the load (output force). The three classes of levers are:
First-class lever: The fulcrum is located between the effort and the load, for example a seesaw or a crowbar.
Second-class lever: The load is located between the fulcrum and the effort, for example a wheelbarrow or a nutcracker.
Third-class lever: The effort is applied between the fulcrum and the load, for example tweezers or a fishing rod.
Questions on levers in a mechanical comprehension test may ask about identifying the class of a lever based on a given scenario or calculating the mechanical advantage of a lever system.
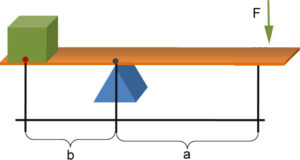
Consider the illustration above and the corresponding data:
Weight = W = 80 pounds
Distance from fulcrum to Weight = b = 10 feet
Distance from fulcrum to point where force is applied = a = 20 feet
How much force (F) must be applied to lift the weight?
a. 80
b. 40
c. 20
d. 10
Answer: B
To solve for F, Weight X b (distance from fulcrum to weight) = Force X a (distance from fulcrum to point where force is applied)
80 X 10 = F X 20
800/20 = F
F = 40
Gears:
Gears are mechanical devices with toothed wheels that interlock to transmit power and motion. They are used to change the speed, direction, or force of rotational motion.
Common questions about gears are, gear ratios, direction of rotation, or calculating the speed of an output gear given the speed of an input gear or gears.
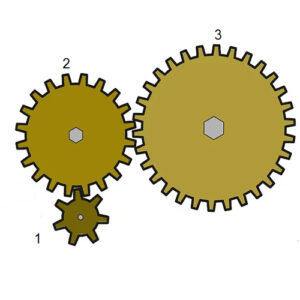
Example Question:
How many turns does gear 1 make when gear 3 makes 210 turns?
a. 30
b. 90
c. 300
d. 900
Answer: D
The equation of meshed gears states that the speed of rotation V (in rot/s) is inversely proportional to the number of teeth N. Mathematically,
N1 ∙ V1 = N2 ∙ V2 = N3 ∙ V3
Here, we are concerned only for the gears 1 and 3. Thus, we have
7 ∙ V1 = 30 ∙ 210
V1 = (30 ∙ 210)/7 = 900 turns
Pulleys
A pulley is a wheel with a grooved rim and a rope or belt running along the groove. Pulleys are used to change the direction or amount of a force, for lifting or moving objects.
Common questions on pulleys in a mechanical comprehension test are calculating the mechanical advantage of a pulley system, determining the direction of the force applied to the load, or understanding the effect of adding more pulleys to a system.
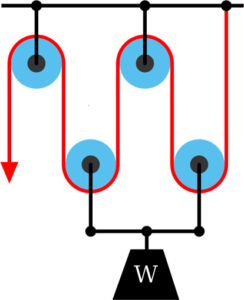
Example Question
Consider the pulley arrangement above. If the weight, W, is 100 pounds, then how much force is required to lift the weight?
a. 100 pounds
b. 50 pounds
c. 25 pounds
d. 20 pounds
Answer: C
Notice the weight is attached to two of the pulleys. The weight required will therefore be 100/4 = 25 pounds.
Spatial Relations
Spatial relations are important on mechanical comprehension tests because they assess an individual’s ability to perceive and understand the relationships between objects in space. Mechanical aptitude tests, which often include spatial relations questions, measure an individual’s capacity to recognize mechanical principles and apply them to various scenarios.
Types of Spatial Relations Questions
Basic Physics
Basic Physics
Testing Fundamental Understanding: Basic physics concepts form the foundation of mechanical principles and phenomena. Including these questions in mechanical comprehension tests allows employers or recruiters to assess candidates’ fundamental understanding of physical and mechanical concepts. By evaluating candidates’ knowledge of topics such as force, gravity, velocity, friction, and energy forces, employers can determine their ability to apply these principles in practical situations. These questions often present real-life scenarios where candidates need to apply physics principles to analyze and solve problems.
Example Questions – Gravity
Which of the following statements about gravity is correct?
a. Gravity is a force that pushes objects apart.
b. Gravity is a force that only affects objects on Earth.
c. Gravity is a force that pulls objects towards each other.
d. Gravity is a force that only acts horizontally.
Answer: C
Explanation: Gravity is a fundamental force that exists between any two objects with mass. It is an attractive force that pulls objects towards each other. This force is responsible for the phenomenon of objects falling to the ground when released from a height. Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
Example Question: Velocity
Which of the following statements best describes velocity?
a. Velocity is a measure of the total distance traveled by an object.
b. Velocity is a measure of how fast an object is moving in a specific direction.
c. Velocity is a measure of the force exerted on an object.
d. Velocity is a measure of the resistance to motion of an object.
Answer: B
Explanation: Velocity is a vector quantity that includes both speed and direction. It describes the rate at which an object changes its position. Unlike speed, which only measures the magnitude of the movement, velocity takes into account the direction of motion. For example, if an object is moving at a constant speed of 30 meters per second to the east, its velocity would be 30 meters per second east.
Physics Practice Questions
Electronics and Circuits
Circuits:
Circuits refer to the paths through which electricity flows. Questions about circuits cover the differences between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), identifying the circuit components of a circuit, or the behavior of circuits in different configurations.
Load
The load is any device or component that consumes power. It can be a resistor, a motor, a lamp, or any other electrical device that utilizes electrical energy to perform its intended function. Questions about loads cover the characteristics of different types of loads or their effects on circuits.
Example Question
In a series circuit, the resistor with the most resistance dominates the circuit.
a. True
b. False
Answer: A
In a series circuit, the total resistance is equal to the sum of the individual resistances. Therefore, the resistor with the highest resistance value will have the most significant impact on the total resistance of the circuit. This means that it will determine the overall behavior of the circuit, and the current flowing through all the resistors in the series will be the same.
Power Source
A power source in electrical systems is a battery, generator, or an electrical outlet connected to an external power grid that provides electrical energy to the circuit. Questions about power sources are, identifying common types of power sources or understand how batteries are connected for different voltage levels.
Example Question
What is the unit of measurement for voltage?
a. Ampere (A)
b. Ohm (Ω)
c. Watt (W)
d. Volt (V)
Answer: D
Voltage is measured in volts (V). It represents the electric potential difference or the amount of energy per unit charge available to move the charges through a circuit.
Conductors
Conductors allow the flow of current through them with minimal resistance, unlike insulators, which impede or prevent the flow of current. Questions about conductors are, identifying materials that are good or poor conductors, understanding their role in completing electrical circuits, or the different characteristics of types of conductors.
Example Question
What is the purpose of a conductor in an electrical circuit?
a. To store electrical energy
b. To provide insulation
c. To regulate voltage
d. To allow the flow of electric current
Answer: D
The main purpose of a conductor in an electrical circuit is to provide a pathway for the flow of electric current. Conductors have low resistance and allow the movement of charged particles, such as electrons.
Start Practicing
Mechanical Aptitude Online Course — Mechanical Aptitude Paperback (Amazon) — Mechanical Aptitude PDF Download
Mechanical Aptitude Tests
Bennett Mechanical
The Bennet Mechanical Comprehension is a psychometric assessment tool used for jobs that require mechanical skills or involve working with machinery or equipment. This is a multiple choice – Help with Multiple Choice
Some common types of questions found in the Bennett Mechanical Test include:
- Pulleys and Gears
- Mechanical Reasoning
- Tools and Instruments. These questions test an individual’s familiarity with common tools and instruments used in mechanical work, such as wrenches, screwdrivers, or calipers.
- Spatial Visualization
The Bennett Mechanical Test is a timed test. How to Manage your Time on a Test
Bennet Mechanical Comprehension (BMCT) Practice Questions and Information
Ramsay Mechanical
The Ramsay Mechanical typical questions are:
- Mechanical Knowledge – basic mechanical concepts, such as gears, pulleys, levers, and simple machines.
- Mechanical Reasoning – mechanical principles to solve problems and may involve analyzing diagrams, identifying mechanical components, or predicting the outcome of a mechanical system.
- Spatial Reasoning – rotating or assembling objects in their mind or visualizing the movement of mechanical parts.
- Tools and Equipment – knowledge of common tools and equipment, their functions and determining the appropriate use.
- Mechanical Drawings – interpreting commonly used technical drawings and schematics, identifying components, understanding symbols, or determining dimensions.
- Calculations – basic mathematical calculations related to mechanical systems, such as calculating gear ratios, torque, or mechanical advantage.
Differential Aptitude Test
The Differential Aptitude Test or DAT is an aptitude test battery for students in grades 7-12 and some adults. The DAT measures various aptitudes – questions include:
- Verbal reasoning
- Numerical ability
- Abstract reasoning
- Perceptual (clerical) speed and accuracy
- Mechanical reasoning
- Spatial relations
- Spelling
- Language usage
Trades Entrance Tests
Trades entrance tests include mechanical comprehension sections to evaluate your understanding of mechanical concepts and principles, how to apply these them.
Mechanical comprehension is a crucial skill for tradespeople who work with machinery, tools, and equipment in industries such as carpentry, plumbing, millwrighting, pipefitting, and more.
Questions include:
- Reading Comprehension
- Basic Math – Includes some basic geometry and algebra
- Mechanical Aptitude
- Spatial Ability
- Basic Science
Trades Entrance Tests
Trades entrance tests that have a mechanical comprehension component:
Start Practicing
Mechanical Aptitude Online Course — Mechanical Aptitude Paperback (Amazon) — Mechanical Aptitude PDF Download
Mechanical Aptitude and Spatial Relations
Mechanical aptitude tests often have a section on spatial reasoning, which measure your ability to mentally manipulate and visualize objects in three-dimensional space. Spatial relations questions are included in test for industries such as engineering, construction, and manufacturing.
Tips for Making the Most of Your Study Time for Mechanical Comprehension Tests
1. Practice. Incorporate practice tests into your study routine. These tests are designed to familiarize you with the types of questions you may encounter and help you improve your mechanical reasoning skills. Practice Questions
2. Understand the concepts Familiarize yourself with mechanical concepts and understand the basic principles behind them so you can answer questions confidently.
3. Get a study guide Use study guides that cover the topic areas typically assessed in mechanical comprehension tests. These guides often include clear explanations and examples, helping you grasp the necessary information efficiently.
4. Pay attention to correct answers and incorrect answers. Look at your answers to practice questions and see where you need to study and where you are OK. After attempting practice questions, analyze the correct answers and the underlying reasons for their accuracy. This will strengthen your knowledge of mechanics and improve your ability to identify the correct answer choices.
5. Manage your study time. Create a study schedule that allocates specific time slots studying. Prioritize challenging areas and dedicate more time to them. Breaking your study time into smaller, focused sessions can improve retention. 20 minutes is optimum.
Date Published: Friday, July 7th, 2023
Date Modified: Wednesday, April 30th, 2025